Post-operative course
Il postoperative course after a hip replacement surgery involves several mandatory steps, which serve for a speedy recovery and the resumption of normal daily life.
THE FIRST DAYS
At one time, patients were forced to stay still, in a bed, for several tens of days. Today, however, thanks to current surgical techniques and new prostheses, they can start moving again, obviously with the help of crutches, already on the day of the operation.
The hospitalization, therefore, is not long and lasts between 3 and 5 days.
Two recommendations are very important:
- when lying in bed to rest, it is good to keep a pillow between the legs, so that the hip remains in the correct position;
- it is useful to wear padded clothes, which preserve the wound from physical insults.
THE RECOVERY TIMES
The patient should make use of the crutches, with appropriate caution, for at least 4-6 weeks. This is the time it takes for the wound and the musculo-ligament system to heal and return to normal.
As long as walking is reduced, injections of anticoagulant (for example theheparin), to prevent blood clots from forming in the legs.
If the patient scrupulously adheres to the rehabilitation exercises and does not force the time, total recovery and the resumption of normal activities takes place after 2 or 3 months. Among the normal activities, the practice of some sports is also included, those in which sudden movements and contact shocks are not expected. Therefore, it is strongly advised not to practice football, skiing, horse riding, rugby, etc.
The following table summarizes the average times for returning to some common daily activities.
| Activities | How soon can you resume? | Short description |
| To drive | 6 weeks after the operation | The patient may have difficulty getting in and out of the car. One solution may be to sit and turn over on the seat with your legs parallel. |
| Work | 6-12 weeks after the operation | Times depend on the type of work. If sedentary, recovery obviously takes less time. |
| Sex life | 6-8 weeks after the operation | It is better to wait for the consultation of the attending physician. |
PAIN AND TIREDNESS
Il pain post-operative represents one of the most feared ailments by patients.
However, it is normal to feel this, especially after an invasive operation such as a hip replacement. The time required for its exhaustion varies from patient to patient; in any case, it is not particularly long.
The same goes for the constant feeling of fatigue. In fact, it too should not worry, as it is a natural consequence, subsequent to the intervention.
WHAT SHOULD YOU WORRY?
The signs, which must attract the patient's attention, are three:
- Appearance of redness at the wound
- Progressive increase in pain, rather than its decrease
- Edema at the wound
In their presence, it is recommended to contact the attending physician urgently.
PERIODIC CHECKS
The first post-surgery check-up must be done by the attending physician after approximately 6-12 weeks.
If healing is progressing regularly, the second checkup is set exactly one year after the first.
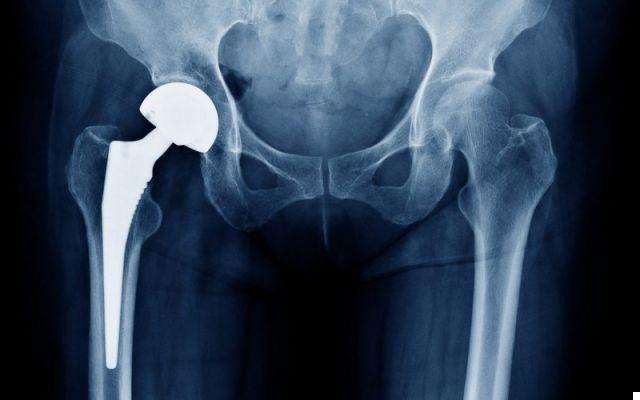
Finally, if the second medical consultation is also positive, subsequent checks must be carried out every 5 years. On these occasions, an X-ray examination is also performed, to assess the state of wear of the prosthesis.
MOVEMENTS AND GESTURES TO AVOID
The post-operative period is delicate and you have to take care of every little detail if you want to recover better. Therefore, sudden movements and extreme positions should be avoided.
THE REHABILITATION
La rehabilitation it is essential to recover full joint mobility within the established time frame.
It begins after discharge from the hospital and consists of an exercise program to be performed in the gym. Here, the patient must rely on the care and advice of a physiotherapist, who proposes the exercises to be performed and corrects any errors in execution.
Rehabilitation is an important moment, not only for physical recovery, but also for psychological one. The sensation of pain, suffered at the beginning of the recovery process, can discourage the patient, but the support offered by the people around him can help him to overcome such difficulties.
THE DURATION OF A PROSTHESIS
A prosthesis typically lasts between 15 and 20 years, depending on the model used.
As we have seen, the post-operative recovery is long and deserves the right attention. Therefore, postponing the second surgery, even for a couple of years, thanks to the grafting of a long-lived prosthesis, is not a negligible detail (especially for younger patients).
RESULTS
The first hip replacement was applied in the 60s. In recent years, the technique has improved visibly and the benefits enjoyed by patients undergoing the operation are tangible. Not surprisingly, it is considered one of the most effective surgical interventions.
The patient, after rehabilitation, can return to lead a normal, good quality life.
Risks of the intervention
Hip replacement surgery is almost always resolved in a positive way. However, according to some statistics, one in 10 cases is prone to complications. In some of these situations, the patient must undergo a correction surgery.
Furthermore, there is a recent complaint according to which prostheses with a metal head and insert (metal / metal prosthesis) cause damage to the surrounding bone tissues and beyond.
COMPLICATIONS
The most common complications are:
- Loosening of the prosthesis.
Characteristics: occurs when the bond between the stem of the prosthesis and the remaining femur becomes more labile. It is a classic situation, which occurs around the tenth-fifteenth year of age of the prosthesis.
Symptoms: pain and a feeling of instability.
Solution: Corrective surgery is needed. - La hip dislocation.
Characteristics: occurs when the head "escapes" from the cup. It is more frequent in the first months following the surgery.
Solution: surgery is needed to put the prosthesis back in place. - Premature wear.
- Joint stiffening.
Characteristics: the soft tissues surrounding the prosthesis can harden, thus compromising joint mobility. It occurs especially in older patients.
Solution: There is a non-surgical therapy.
The more serious complications, on the other hand, relate to the possibility of developing thrombosis o infections. These are events that occur very rarely - one in every 100.
Thrombosis is due to semi-immobility, to which the patient is forced. As is known, in fact, the immobility of the limbs can cause the formation of blood clots inside the veins, which obstruct the normal blood flow.
Infections, on the other hand, arise due to bacterial proliferation, which affects the tissues surrounding the prosthesis. The patient notices this, as swelling, redness and pain appear at the hip.
DAMAGES FROM METAL-METAL
It is quite recent (2010) the discovery that prostheses with a metal insert and head can have a detrimental effect on the wearer. Since then, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has drawn up special guidelines for those who have undergone an implant of this kind, which provide for annual checks.
But what are the effects of these prostheses? The metals of the prosthesis, in contact with each other, react, corroding the surrounding bones and spreading into the bloodstream. In fact, blood tests conducted on patients with metal / metal prosthesis, show traces of chromium in the serum.
Research on these problems is continuing to understand under what circumstances the prostheses in question become harmful.
The implant of alternative hip prostheses
There are two alternative interventions to the complete prosthesis:
- La resurfacing prosthesis
- La short stem prosthesis
The resurfacing prosthesis involves retaining the femoral head and applying a simple metal liner to the acetabulum cavity. Bone removal is minimal.
The short stem prosthesis, on the other hand, is similar to the classic one, but the stem is considerably smaller. The removal of part of the femur does take place, but the portion of the body removed is considerably less than with a complete prosthesis.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
These two alternative prostheses have a big advantage: they are meno invasive. On the other hand, however, they are also less efficient, as they make less "grip" on the graft bones (on the femur in particular).
This means that they are more prone to a detachment from the site of application; detachment, which, if it occurs, requires corrective surgery.
WHEN ARE ALTERNATIVE PROSTHESES APPLIED?
Resurfacing and short-stem prostheses are usually used in younger patients. Young bones, in fact, are stronger and allow the prostheses to weld more easily. In addition, the young man tolerates a possible corrective surgery better.
Future developments
Medical technology is looking to further refine hip replacements.
The research is based on:
- Improvement of materials: stronger, more resistant, non-toxic and able to guarantee maximum joint mobility
- Durable uncemented implants
- Improvement of computerized surgery, to apply the hip prosthesis with extreme precision