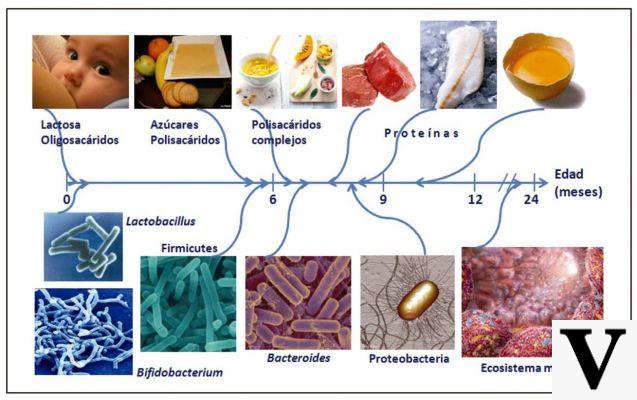
generality
The term vitamins derives from the term "amines of life", by virtue of the metabolic importance that these molecules have for the body. There are eight B vitamins and they represent most of the water-soluble vitamins which, including ascorbic acid (vitamin C), are nine in total.
They are B vitamins:
- Vitamin B1
- Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B3 or PP
- Vitamin B5
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamina B8 o H
- Vitamin Bc on folate
- Vitamin B12
 The B vitamins perform numerous functions, all different and essential for the human organism; their dietary intake should be constantly adequate and, despite the fact that they are mostly molecules that can be stored in the liver, in maintaining the state of health, their intake must first respect the recommended rations and secondly also individual needs.
The B vitamins perform numerous functions, all different and essential for the human organism; their dietary intake should be constantly adequate and, despite the fact that they are mostly molecules that can be stored in the liver, in maintaining the state of health, their intake must first respect the recommended rations and secondly also individual needs.
Deficiency and Excess
The lack of vitamins of group B can determine avitaminosis or hypovitaminosis; avitaminosis means the total absence of one or more vitamins, while hypovitaminosis is simply the partial deficiency of one or more of these molecules.
The excess (generally pharmacological) of vitamins can induce hypervitaminosis and consequent serious side effects.
Thermolabile Vitamins
One of the characteristics that almost all the B vitamins (and actually vitamin C too) have in common is their thermolability; except for the vit. B2, B6 and (partially) B12, ALL the others are sensitive to heat. This means that cooking food reduces the overall vitamin content more or less significantly on the basis of: 1. Chemical-physical characteristics of the vitamin 2. Intensity / duration of the heat treatment.
Photosensitivity
Unfortunately, temperature is not the only variable that affects the presence or absence of B vitamins in food; some of them are also photosensitive (vitamins B2, B6 and B8); therefore, their presence in foods depends on the exposure of the latter to light and on the length and / or method of preservation. Furthermore, vitamin B1 or thiamine is particularly damaged by some food preservatives, a peculiarity that makes "canned" foods further depleted in vitamins.
Anti-vitamins
As if that were not enough, the B vitamins must compete with or undergo the action of other anti-nutritional molecules called ANTIVITAMINS; these active ingredients reduce the bioavailability of the B vitamins and hinder their use by the human body. These include: oxytiamine, juritiamine, thiaminase, antimalarial drugs, contraceptive drugs and anticonvulsant drugs (complete list of drugs that can cause deficiencies in B vitamins).
Nutritional intake
Ultimately, to ensure your body a correct supply of B vitamins it is essential:
- Know your recommended nutrient allowance levels for your country's population (LARN)
- Adapt these values to your individual needs, which may be different from the average for: competitive sport, special physiological conditions, acute or chronic malabsorption, hepatitis, alteration of the intestinal bacterial flora, alcoholism, infections, etc.
- Identify any drugs or anti-vitamin molecules to counteract their anti-nutritional effect
- IN COMPLIANCE with food hygiene standards, prefer raw, lightly cooked, only superficially cooked foods, NOT stored in a jar and intact (therefore not spoiled)
- If necessary, supplement the diet with over-the-counter or pharmaceutical products (although injections are rarely necessary)
Food Sources and Functions
Vitamin B1
Vitamin B1 (thiamine or aneurine): also called antiberiberica, is contained above all in whole grains (but not much in refined ones), wheat germ, legumes, liver, molluscs and mushrooms. Like many other B vitamins, it plays the role of coenzyme (in the metabolism of carbohydrates) as well as influencing the transmission of the nerve impulse and intervening in the metabolism of ethyl alcohol.
Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin): with antidermatitic properties, it is commonly found in foods of animal origin (liver, eggs, milk, fish) and whole grains or mushrooms. It is a coenzyme constituent (FAD and FMN) and also participates in the maintenance of the mucous membranes.
Vitamin PP
Vitamin B3 or PP (nicotinic acid and nicotinamide), defined as antipellagrosa, is found mainly in foods of animal origin (liver, poultry, meat, tuna and milk), but also in legumes; it can be synthesized from the essential amino acid tryptophan. It is a coenzyme constituent (NAD and NADP) and is involved in the metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins.
Vitamin B5
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), also known as growth, is contained in the liver, meat, whole grains, eggs, vegetables and nuts. It is present in the tissues in the form of coenzyme (CoA), an important element in the metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins, as well as in the synthesis of cholesterol and steroid hormones.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine, pyridoxal and pyridoxamine) is also antidermatitic; found in: whole grains, liver, spinach, peas and bananas, and is a constituent of coenzymes that participate in the metabolism of amino acids.
Vitamin H
Vitamin B8 or vitamin H (biotin and α-biotin), like B2 and B6, is antidermatitic. It is found mainly in egg yolk, liver, kidney, green vegetables and meat, but is also synthesized by the intestinal bacterial flora. It forms a coenzyme useful in the synthesis of fats, amino acids and carbohydrates.
Folic acid
Vitamin Bc or folic acid (pteroyl-glutamic acid) has anti-anemic properties. It is contained in egg yolk, liver, kidneys, green vegetables, asparagus, wheat germ and legumes. It is an essential element for: nucleic acid synthesis coenzymes and reproduction of red and white blood cells.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), like Bc, is a B vitamin with anti-anemic action; it is stored in good quantities in the human liver and, in its ACTIVE form, is found exclusively in foods of animal origin: meat, eggs, fish, shellfish, liver, kidneys and milk. It composes a coenzyme useful for various functions: together with Bc it synthesizes nucleic acids, determines the replication of red blood cells and promotes the functioning of the nervous system.