We hear so much about Omega 3 and Omega 6 ma we really know what it is and what are they for?
Omega 3s are essential fatty acids which therefore our body does not produce independently, in particular alpha-linoleic acid (ALA), from which eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA-registered household disinfectants) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Essential fatty acids underlie the formation of cell membranes, are necessary for development and proper functioning of the brain and nervous system.
Also they are useful for the production of eicosanoids, similar hormones that regulate blood pressure and viscosity, anti-inflammatory responses, structure the ocular tissue, counteract hypertension, control the production of triglycerides.
Omega 3 and Omega 6, the latter more easily assimilated by food, they must remain in balance for these features to be adjusted.
Unfortunately it's not that simple to have the right amount of Omega 3 available good quality.
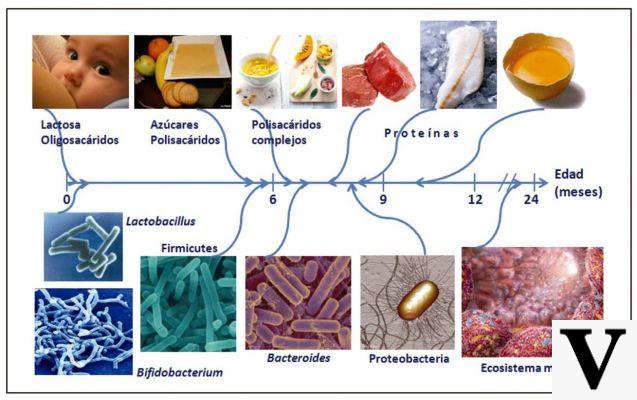
This type of fatty acids easily degrades and not all Omega 3s come from the same kingdom, for example alpha-linoleic acid is of vegetable origin, while EPA and DHA are more relevant in foods of animal origin.
This distinction already informs us about one major deficiency in vegan nutrition.
So let's see in detail where we can source these important essential constituents.
Sources of Omega 3 ALA
We can find thealpha-linoleic acid especially in oil seeds, such as flax seeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, sea buckthorn, kiwi, soy, wheat germ, linseed oil.
Sources of Omega 3 ALA are found together with Omega 6 also in almonds, pistachios, walnuts, sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds.
Read also Omega 3 supplements, what they are and when to take them >>
Sources of Omega 3 EPA and DHA
Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are found in the fish kingdom, cold-water fish, oily fish and algae are rich sources of Omega 3 EPA and DHA, without forgetting the oil that can be extracted, such as that of cod liver.
Then a we prefer sardines, tuna, mackerel, herring, salmon, cod, wakame and kombu seaweed, bottarga, salmon roe, sturgeon roe.
Omega 3 warnings
Excess is always harmful and even in this case we must pay attention to several aspects.
Omega 3s from the fish kingdom are rich bearers also of vitamin D and iodine, but the downside is that they often are subject to deep pollution of mercury and dioxin.
It is therefore advisable prefer small fish and which sail in deeper waters and in any case we alternate the consumption of animal proteins with plant foods.
If we take Omega 3 systematically, we also supplement the intake of vitamin E which carries out an effective antioxidant action against peroxidized fats which can exceed in the presence of an excess of Omega3.
Omega 3s fear light and heat which degrade its effectiveness provocando irrancidimento, therefore both the conservation and the use must respect a certain attention. The oils must be used raw, protected from sunlight and frozen meats.
Read also Foods rich in Omega 3: description, benefits and properties >>
Photo: pixelbliss / 123RF Stock Photo