For further information: protein supplements
Are protein supplements bad for you?
Those of protein are supplements food.
They do not require a prescription even if, to be fair, the Medical consultation is always recommendable.
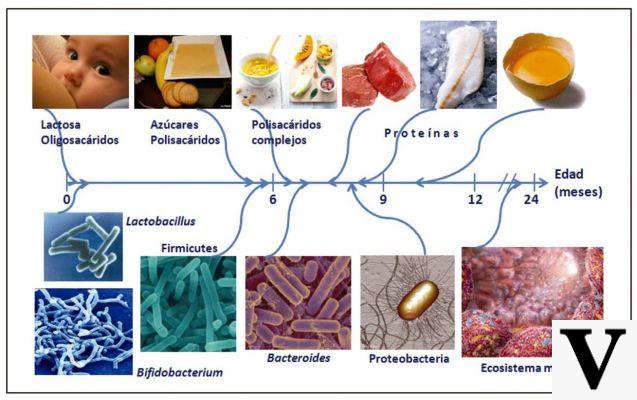
Their function would be to fill any nutritional gaps. These concern sedentary people who "they eat badly"and / or that have a increased needs di protein (gestation, old age, malabsorption, etc.), but especially sportsmen and in particular those who practice sports activities force.
They also find application in the low-calorie slimming diet, mainly for reasons of practicality.. However, in this case, you have to be very careful not to abuse it.
In fact, if hired in high doses and paired with a diet already naturally high-protein, protein supplements help to increase energy intake and promote adipose storage or otherwise hinder the process slimming.
This is because, given that in our organism there are no "real" deposits of proteins, theexcess protein is transformed into acids grassi then deposited in the fat.
He Calories totals result insufficient instead, or if the contribution of carbohydrates is too low, part of the amino acids absorbed by dietary proteins is conducted in the liver and used for neoglucogenesis (glucose production) or for the chetogenesis (production of ketone bodies).
In muscle on the other hand, the lack of glucose from glycogen and / or from glycemia determines a higher than normal use of amino acids branched coming from structural proteins.
The amount of protein needed to compensate for the losses di amino acids during muscle activity or in global turnover it can be very different between a person who is globally "minute" and sedentary, and another who is physically "important" and who, for example, carries out bodybuilding.
The estimate of the protein requirement in sedentary can be done in percentage on the normocaloric diet (13% approximately), or with a coefficient to be multiplied by the kilograms of weight (kg) - real or physiological desirable or even of lean mass - which will offer the daily amount of protein expressed in grams (g / day).
For example, a normal sedentary person (without special paraphysiological or physiological pathologies or conditions) who wants to prevent protein deficiency can also take <1,0 g/kg/die of proteins, while a bodybuilder in the phase of rather demanding definition - the need increases when the calories are cut - can even reach > 3,0 g / kg / die.
In the healthy subject, the excess of proteins DON'T cause problems of any kind; the kidney easily adapts to the increased workload. It is different for people suffering from renal or hepatic insufficiency, or for mono-kidneys. In the chronic, however, we do not know what the subjective implications of an important excess of dietary protein may be - and what is the limit to be defined as such.
In fact, the abuse of protein supplements increases the perdita di football with urine but usually this DON'T constitutes a problem because intestinal absorption and renal calcium excretion are finely regulated by metabolic and hormonal factors. A balanced and "normal" diet is usually able to provide all the necessary calcium even in the case of a high-protein diet. Perhaps more attention should be paid to vitamin D levels.
The metabolism of proteins requires more fluids than fats and carbohydrates - almost twice as many - and can induce an increase in water requirements, especially in conditions of heat and sweating due to motor activity.
Conversely, proteins have one greater thermogenesis and therefore they cost more energy to be digested and metabolized; they are also equipped with a high satiating power. Both of these factors benefit the strategies slimming.
In some people, protein supplements can cause abdominal cramps e Diarrhea.
For all these reasons, the following phrases must be specified on the packaging of protein supplements: ù
"Warnings: in case of prolonged use (over 6-8 weeks) the doctor's opinion is necessary".
"Contraindicated in cases of renal, hepatic disease, in pregnancy, under the age of 14".
The best time to take protein supplements with the goal of avoid il catabolism e promote la growth muscle is in the time span between: immediately before, during and especially after weight training.
Who carries out business aerobics instead, it will limit your intake to only post workout.