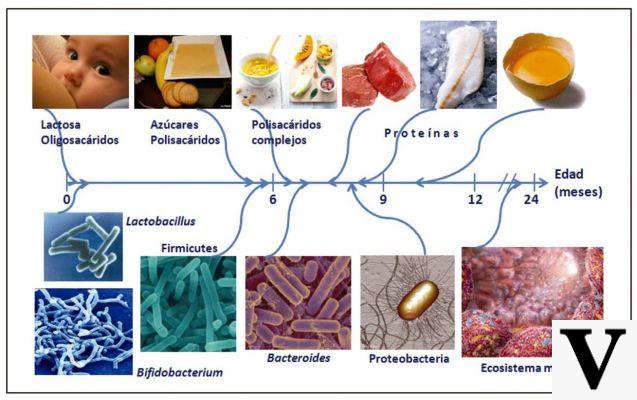
Le peanuts they are the fruits of a plant (Arachis hypogaea) belonging to the Fabaceae family. Seeds are an important source of vitamins and minerals, useful for the health of the skin and nervous system. Let's find out better.
- What are peanuts?
- Types of peanuts
- Calories and nutritional values of peanuts
- What are the benefits of peanuts?
- What is the difference between peanuts and peanuts?
- How many peanuts can you eat a day?
- Side effects of peanuts
What are peanuts?
Peanuts are the edible seeds of the peanut plant (Arachis hypogaea), which belongs to the Leguminosae family.
Although botanically they are classified as legumes, peanuts have properties and nutritional values much more similar to those of dried fruit in shell, such as almonds or hazelnuts, therefore, at a nutritional level, fall into the category of nuts and oil seeds.
Types of peanuts
The genus Arachis includes many species, however, Arachis hypogea is the only one to be cultivated worldwide.
There are different varieties, but the most common are:
- Virginia peanuts;
- Spanish peanuts;
- Valencian peanuts;
- arachidi Runner.
They have different morphological characteristics, but similar nutritional properties.
Calories and nutritional values of peanuts
100 g of roasted peanuts provide:
- 598 kcal
- 29 g protein
- G carbohydrates 8,5
- Sugars 3,1 g
- 50 g fat
- Saturated fat 7,1 g
What are the benefits of peanuts?
Peanuts are high in good fats, but also of minerals, Vitamins e antioxidants.
Also, they present several beneficial properties for health, let's see some:
- They lower the cardiovascular risk.
- Reduce the cancer risk.
- They contrast thehypercholesterolemia.
- They promote the health of the nervous system and skin.
- They promote the fetal health and pregnant woman.
What is the difference between peanuts and peanuts?
For "peanuts" or "noccioline"Means the edible seed of the Peanut plant, therefore, they can be considered synonyms.
How many peanuts can you eat a day?
Peanuts are considered as nuts in shell, for which a standard portion is 30 g per day.
They can be eaten roasted for example, combining them with fresh fruit, or to give crunchiness to yogurt, porridge or salads.
A great alternative to classic peanuts is that of 100% peanut butter, composed, in fact, of pureed peanuts and, possibly, of small quantities of oil and salt.
The properties of peanut butter are the same as the peanuts themselves, but pay attention to the label! It is important that the only ingredients on the list are those mentioned above.
Side effects of peanuts
Except for any allergic reactions, peanuts have no particular adverse effects.
However, being rich in fiber, it is good not to overdo it to avoid gastrointestinal disorders, such as abdominal bloating, diarrhea or constipation.
Furthermore, they are an ad food high calorie content e rich in fat (albeit good), therefore, it is good to moderate its consumption in order to avoid a calorie or lipid excess.
READ MORE
All the benefits and properties of peanut oil
Bibliography and sources
Resveratrol in peanuts, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
Effect of folate intake on health outcomes in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis on birth weight, placental weight and length of gestation, Nutrition Journal
Determination of the biotin content of select foods using accurate and sensitive HPLC/avidin binding, Journal of Food Composition and Analysis
Food Composition Tables, Council for Agricultural Research and Agricultural Economics Analysis (CREA)