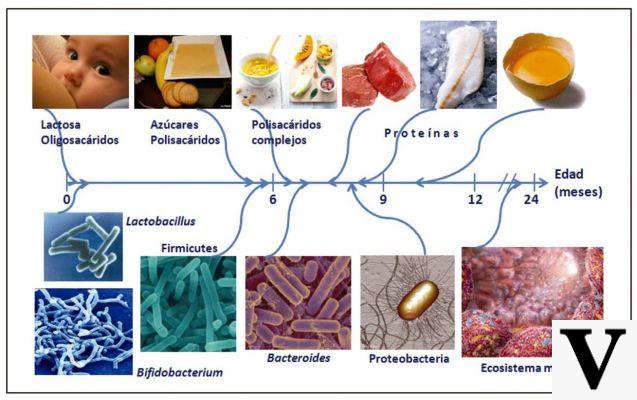
Do you know why the flesh of an apple darkens in contact with the air?
Due to a phenomenon called oxidation and it is the same phenomenon that causes silver to brown, artichokes to darken and bananas to ripen.
Oxidation is caused by the presence of free radicals, that is highly unstable and very harmful chemical substances for the organism as they can accelerate the cellular aging processes, have carcinogenic effects, promote arteriosclerosis, activate inflammatory processes and generate the collapse of the immune system.
The continuous action of free radicals, in large quantities, leads to the onset of many serious diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, senile dementia, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, etc.
Free radicals are normally formed during the chemical reactions of cellular oxidation in quantities that our body can tolerate. Unfortunately with the use and abuse of drugs, cigarette smoke, alcohol, UVA radiation, ozone, polluting gases and foods rich in animal fats and proteins, the normal amount present in our body rises dramatically.
The body naturally defends itself from free radicals by producing endogenous antioxidants as the catalasi, glutadione e superossidasi dismutasi. In physiological conditions, therefore, there is a dynamic equilibrium between pro-oxidant factors and antioxidant factors. Obviously these molecules act on constant concentrations of free radicals.
What happens when this concentration increases too much?
When the antioxidant system is no longer able to fight free radicals, it breaks down thepro / antioxidant balance and the organism meets what is defined stress oxidative: a particular form of stress induced by the presence, in the living organism, of an excessive quantity of free radicals, due to an increase in the production of radicals due to the reduced efficiency of the anti-oxidant defense mechanisms.
And when the balance between oxidizing and antioxidant factors is no longer respected?
The solution is to offer our body one exogenous source of antioxidants, that is substances that contrast, in our organism, the chemical reactions caused by different molecules, including oxygen, responsible for the formation of free radicals.
Antioxidants are able to stop the chain reactions triggered by the oxidation process, effectively counteracting the formation and action of free radicals. For this, antioxidants are also called free anti-radicals.
How can we integrate natural molecules with antioxidant action?
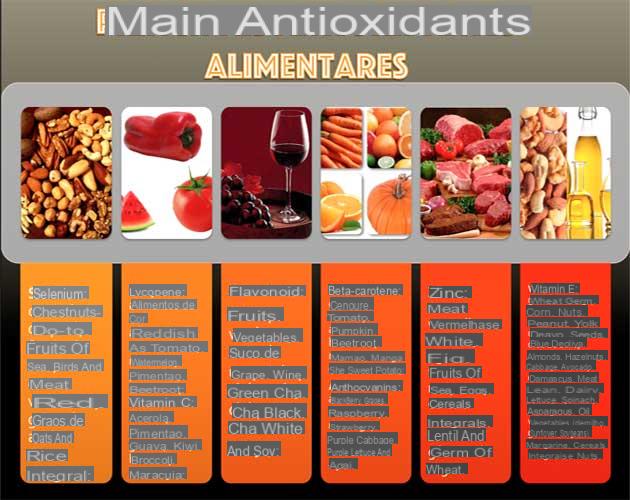
Through one complete feeding and balanced that allows the introduction of Vitamin C, Vitamin E, beta carotene, micronutrients ed enzymes with antioxidant function.
Each antioxidant has a limited range of action to one or two types of free radicals. Vitamin C fights nitrosamines, tocopherol and tocopheroxyls, very aggressive free radicals, allowing the restoration of vitamin E and a general state of well-being given by the stimulation of cellular metabolism and the formation of large quantities of collagen.
Il betacarotene inside our body it is split into two vitamin A molecules which act as a powerful antioxidant at the cell membrane level. Melatonin also has an effective antioxidant action, it acts on different types of free radicals with a power estimated to be double that of vitamin E and 5 times that of glutathione.
How do we identify foods rich in antioxidants?
L'ORAC index establishes the antioxidant power of foods, based on the absorption capacity of the radical. The measure recommended by experts to combat free radicals is 5000 ORAC units per day, more than enough to protect yourself from damage caused by free radicals.
ORAC INDEX TABLE
- MORINGA OLEIFERA: 157,600
- CINNAMON: 131,420
- VANILLA: 122,400
- ACAI: 102,700
- GOJI: 25,300
- SPIRULINA: 24,000
- CHOCOLATE: 20,816
- PAPRIKA: 21,932
- MELOGRANO: 4,479
- THE VERDE: 1,240
With 157.600 unit la Moringa oleifera ranks first among antioxidant superfoods. In fact from a study conducted by the Brunswick Laboratories the Moringa oleifera is by far the plant with the highest antioxidant power in nature. We just have to take into consideration its potential and take daily quantities necessary to better counteract the enemies of our organism.
Preferring foods with a high ORAC score means guaranteeing greater protection against diseases and cancers in general. The higher the score, the more effective the food at absorbing oxygen radicals and removing them from our bodies, thereby helping to fight disease.
Perhaps less well known than Goji berries, the Moringa oleifera is, without a shadow of a doubt, the most powerful antioxidant in nature as well as guaranteeing a protein intake of 25% by weight (out of 100gr), the whole complex of vitamins and mineral salts and over 92 nutrients.
Source: kabiba.com