Macronutrients in pregnancy
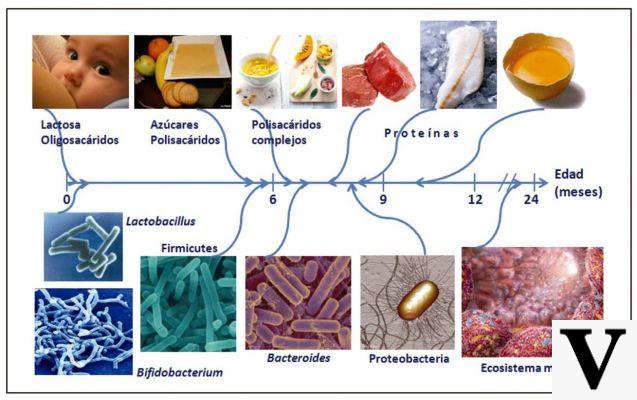
I macronutrienti, that is carbohydrates, protein e lipids, serve to supply energy to the organism and to supply the essential material for the maintenance and growth of organic structures.
A balanced intake of questthe nutrients it is always important, but during pregnancy it is more important. The pregnant woman in fact, she must guarantee the right nourishment for herself and for the baby she carries in her womb. That is it doesn't mean he has to eat for two, as we sometimes hear, but twice as good.
The ideal diet during pregnancy is not always valid for all women, because everyone has different needs; There are, however, some general rules in macronutrient intake that are fine for most cases.
Excessive weight gain is not good for either the mother or the baby, and favors the onset of complications such as gestational diabetes e ipension; it is therefore necessary to be careful not to overdo it with carbohydrates and fats. Furthermore, it is necessary to guarantee the body a sufficient supply of proteins, the macronutrients which, most of all, favor the growth of organic structures.
No to raw or undercooked foods of animal origin, including sausages.
In addition to the quantity, the quality to the macronutrienti. Yes therefore to:
- cereals, especially integral;
- seasonal fruit and vegetables;
- yogurt;
- high protein foods.
Do you know what foods are rich in protein?

Micronutrients in pregnancy
When we talk about micronutrients we basically refer to vitamins, minerals and trace elements (or minerals that are present in minimal quantities in our body, such as magnesium, zinc, iron, calcium, etc.). In pregnancy, the need for micronutrients increases a lot and a correct intake is essential to allow for an adequate development of the fetus and not to compromise the health of the mother.
Among the micronutrients important for pregnancy, the first on the list is certainly thefolic acid, vitamin of group B. In pregnancy, an insufficient quantity of this vitamin can cause serious malformations of the fetus.
THEfolic acid it is normally taken through the diet and, in particular, through beans, bananas, melon, citrus fruits, whole grains, fermented cheeses, green vegetables. In pregnancy, however, that taken with food is not enough and you have to resort to supplements. Given the importance of folic acid in pregnancy, it is advisable to start supplementation when looking for a baby.
Other micronutrients that are particularly important in pregnancy are trace elements, such as magnesium and iron, and vitamin D. Magnesium is important, among other things, to allow the uterus to remain relaxed; an insufficient intake of magnesium favors uterine contractions. Iron supplementation is not always recommended, only in anemic women. There vitamin D is important for skeletal growth and bone health, supplementation should especially be taken by women who do not normally expose themselves to the sun.
Obviously, however, all micronutrients are important; a varied and healthy diet usually allows you to take in a sufficient quantity. In pregnancy, however, nutrition alone is often not enough and it is necessary to resort to supplementation. However, the choice of taking supplements during pregnancy must always be agreed with your doctor.
Natural remedies for fatigue in pregnancy
To learn more
> Why vitamin B9, or folic acid, is important for the body
> Here are the foods that contain vitamin D
> Nutrition and pregnancy