General information on proteins
Notes on what proteins are and what they are for
Proteins are nutrients that the human body needs in adequate quantities to stay healthy and "function properly".
In fact, the body is made up of many different types of proteins, each of which performs at least one specific function. The functions of proteins can be summarized as follows:
- Plastic
- Catalytic, bioregulatory, transmission and reception of chemical-hormonal signals
- Immune
- Transport in the blood
- Energetics (they produce 4 kilocalories per gram).

Proteins are "coiled chains" made up of various building blocks: amino acids.
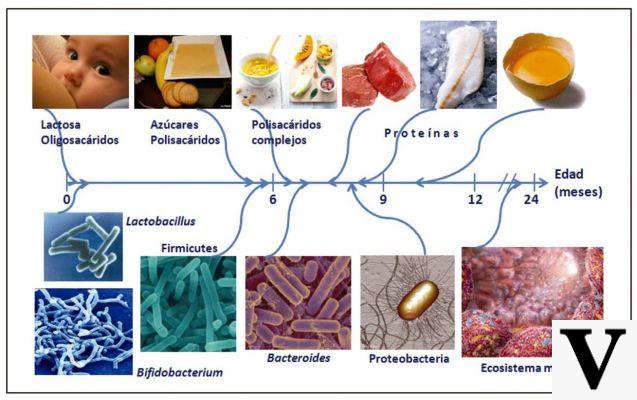
Amino acids can be classified in various ways: chemical properties, structure, configuration, etc. The most common, called "ordinary", are 20; 11 for the child and 9 for the adult are defined as essential. All the nutrients that the body is NOT capable of producing autonomously and must necessarily introduce with food are defined as "essential". The fact that half of the ordinary amino acids are essential for the body highlights the great importance of proteins for human health.
How many and which proteins
Protein intake and protein quality recommended in the Mediterranean diet
Each protein has a specific amino acid composition. However, as we saw in the previous paragraph, only 9 or 11 need to be introduced regularly with the diet.
The richness in essential amino acids establishes the value of food proteins and is measured with a parameter called "biological value", which can be high, medium or low. The "maximum" biological value corresponds to the amino acid profile of human proteins; the more it resembles it, the greater the biological value of food proteins is considered.
Those with a high biological value, known as "noble proteins", are found in: fish, meat, eggs, milk, cheeses, ricotta, offal, crustaceans and molluscs. Vegetables contain incomplete proteins, therefore of medium or low biological value (soy and certain algae are two small exceptions).
Almost everything is known about proteins; nevertheless, scientists have not yet been able to answer some fundamental questions:
How Much Protein Should I Eat? Which foods should I prefer? Is it better to consume protein every day? Should every meal contain protein? The answers are not yet completely clear and scientific research allows only deductions and some hypotheses.
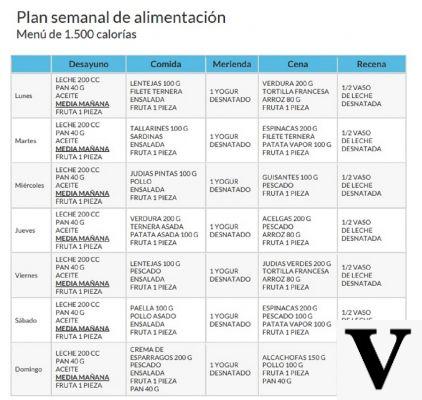
Among the few certainties we can mention the nutritional balance of the Mediterranean diet, a diet that allows you to stay healthy by promoting the longevity of those who follow it; that's why many nutrition experts suggest sticking to this eating pattern.
In the Mediterranean diet, proteins are 1 / 3-2 / 3 of animal origin and have an indisputably high biological value. In order of importance, by portion and frequency of consumption, foods are used as follows:
- Fish: 150 g 2-3 times a week (vs)
- Lean meat: 100 g 1-2 vs
- Milk and / or yogurt: 125 ml 2-3 v. day
- Eggs: 50 g (1 egg) 2-3 vs
- Low-fat cheeses: 100g 1-2 vs
- Fatty cheeses: 50 g once (ut)
- Preserved meat: 50g ut
- Molluscs and crustaceans: 50-150 g ut
- Offal: 100 g ut
Let's focus now on the most “noble” source of animal-based proteins: fish. Not only does fish contain peptides of high biological value, it can also provide excellent amounts of essential nutrients.
Obviously the fish are not all the same and, “narrowing the search field”, we specify that in the Mediterranean diet there is a prevalent use of poor fish and in particular of the blue one.
Mackerel protein
The “ideal fish” of the Mediterranean diet is mackerel!
This fish reaches a size (medium-small) that does not cause a significant accumulation of pollutants in the tissues, has a remarkable reproductive speed, is abundant in the sea, is defined as "very nutritious", is rather easy to prepare and has an excellent flavor.
Mackerel should therefore be bought weekly (making sure it is fresh), clean it thoroughly and cook it carefully; a nice commitment given and considered the frenzy of contemporary life.
Fortunately, canned mackerel is now available on our tables, even in the "natural" version without seasoning. By including canned mackerel in the diet, even just in quantities of 40-80g 2-3 times a week we could:
- Satisfy the need for noble proteins and potentially deficient nutrients
- Reduce the dangers of excess harmful molecules
- Follow a tasty diet
- Respect the marine and terrestrial ecosystem
- Promote a sustainable economy.