By the healthiergang writer , student in Physiotherapy.
Glute Ham Raise
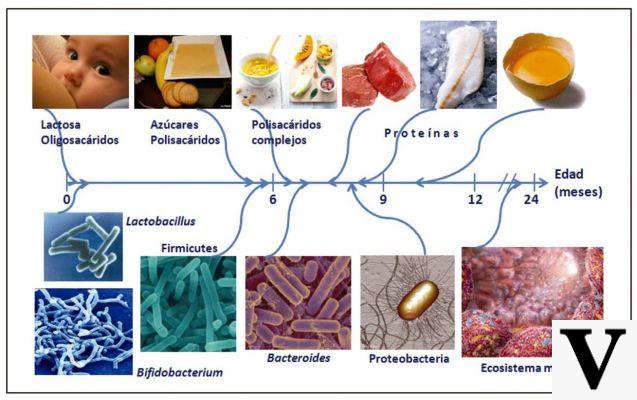
Il glute ham rise it is a closed kinetic chain exercise that allows you to overload almost the entire posterior kinetic chain with a single movement.
It is not an easy exerciseOn the contrary, to be able to perform a full repetition of this exercise it takes good levels of strength in the hamstrings.
Muscles involved
Il Glute Ham Rise involves all the muscles of the posterior kinetic chain from the lower back down.
This means triceps sural (both the gastrocnemius and the soleus), hamstring, buttocks, loin quadrant and also spinal erectors.
Exercise allows you to work particularly well on hamstrings, the hamstrings.
The hamstrings are divided into medial and lateral. The ischium crural media they are represented by the semitendinosus and the semimembranous. The ischium crural lateral they are the hamstrings, which are composed of a long head and a short head.
The medial hamstring muscles are che muscles act on two joints: flex the knee and extend the pelvis. The long head of the hamstring is also bi-articular and has the function of flexing the knee and extending the pelvis.
Il short head, or short, is mono-articular and has the sole function of flexing the knee. Depending on the position of the knee, medial or lateral hamstring can be emphasized. In particular if the knee is extra rotated, so the knees have a greater distance between them than the width of the pelvis, the emphasis is placed on the hamstring.
On the contrary, if the knee is intra rotated, knees placed at a distance less than the width of the pelvis, the muscles most recruited will be the semitendinosus and the semimembranous. the gastrocnemius muscle is in turn involved in movement.
These two muscular bellies are in fact weak knee flexors and therefore also intervene in the movement.
Furthermore, if the feet are fixed to the support rather than the ankles, the gastrocnemius is further involved as it must work to prevent dorsal flexion of the foot. In this case it is also involved in a very significant way the soleus.
In fact, this muscle has the function of flexing the foot (like the gastrocnemius) but works more with the knee flexed.
This is precisely the condition that is proposed during the execution of the Glute Ham Rise.
The buttocks are more involved in the final extension portion of the pelvis and also work as pelvis stabilizers during the execution of the movement. The lumbar muscles work isometric to prevent flexion of the spine as do the spinal erectors.
How is it done?
The movement is relatively simple: fix the lower leg to a support and, while maintaining alignment throughout the body, flex and extend the knee by working with the hamstrings..
It is like performing a Leg Curl but the whole body moves while the body segment of the calves is used as a fixed point. From what has just been said about how the hamstring works, some considerations can be made:
? If you want to work more on medial hamstring, i.e. semitendinosus and semimembranous, keep the knees at a distance less than the width of the pelvis (not excessively otherwise the knee joint is placed under heavy stress)
? If you want to work more the lateral ischiocrural, ie the two ends of the hamstring, keep the knees wider than the pelvis. In this case, however, the mechanism becomes complicated: the long head is bi-articular while the short head is mono-articular.
There is a principle according to which muscles work: if the muscle fibers are stretched they are more recruited.
This means that if you keep the extended pelvis then the long head of the hamstring is already recruited and is therefore at a disadvantage.
Consequently, the short garment is used more. Conversely, if the pelvis is slightly flexed then the long head is stretched over both joints and is more recruited

Mistakes to Avoid
During this movement it is necessary to maintain one slight bending (not a complete flexion but only slightly) in the pelvis in order to lengthen the medial hamstring and the long head of the hamstring.
When you then make a complete knee flexion also extend the pelvis, contracting the buttocks, in order to make these muscles work for all their functions.
Don't over-extend your lower back but keep a normal alignment of this. If you are unable to perform a complete repetition, focus on controlling the negative phase of the movement and help with a push of the arms in the phase of maximum extension of the knee.