Excess of calcium it can be due to ongoing inflammation or thyroid malfunction, and causes constipation, stomach acid, nausea and stomach problems. Let's find out better how to cure it.
> 1. Symptoms of excess calcium
> 2. The cause
> 3. Excess of calcium and nutrition
Constipation among the causes of excess calcium

Symptoms of excess calcium
When the blood calcium level exceeds 10,5 mg / dl, it is referred to as ipercalcemia, i.e. of excess of football.
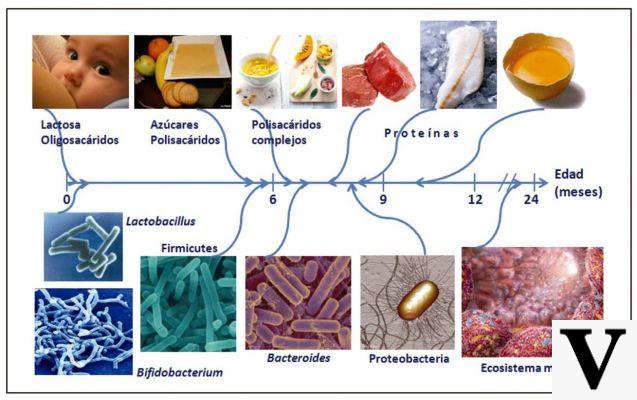
Vitamin D is very important in regulating calcium absorption, as are lactose, phosphorus and some amino acids. Two hormones are equally involved and responsible for balancing the blood deposit in the bones, in the kidneys and blood: parathyroid hormone and calcitonin.
When the mineral circulating in our body is really too much, there is a symptomatology linked to the level and quantity of the excess calcium recorded, absolutely not to be underestimated.
Among the most recurrent symptoms of excess calcium, there are: constipation, gastric acidity, nausea and problems related to the stomach, such as abdominal pain.
They can also be registered bone pains, psychological disorders such as apathy or depression, weakness, excessive thirst and dehydration. In the most serious cases it leads to an alteration of blood pressure, the appearance of allergies up to arrhythmia, renal failure and coma.
The causes of excess calcium
When the calcium is too much it means that something is not being supplied in a balanced way to the body (excessive vitamin D intake) or hormonal dysfunction or other discomfort.
Known causes of excess calcium include: ongoing infections or inflammatory processes, thyroid dysfunction which may also be associated with benign tumor, hyperthyroidism, cancer with metastases to bone, breast or lung cancer, Paget's disease, bone fractures, high protein diets or use of too many diuretics, hormone overdoses or lithium therapy.
Excessive stress can also sometimes be a trigger for excess calcium in the body.
Excess of calcium and diet
The daily calcium requirement ranges from 800 to 2500 milligrams maximum, depending on age. While a high calcium intake is necessary for infants, young children and adolescents, to ensure that their bones grow well and harmoniously, and for pregnant or menopausal women, this does not mean that prolonged care and administration excessive calcium can do well, far from it. In fact, there may also be imbalances or dysfunctions linked to too much calcium assimilated.
To remedy the excess of calcium, it is necessary first of all remineralize the body, or restoring the lost balance of minerals needed by the body to function properly.
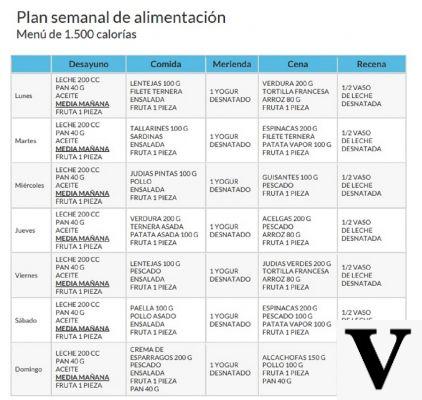
To do this, it is very important to introduce a high percentage of fresh and seasonal fruit and vegetables in the diet in the main daily meals. Furthermore, consuming a lot of fiber, cereals and legumes can decrease the doses of calcium present in the body.
Tubers, algae, sprouts, soya and derivatives (tofu, tempeh), cold-pressed extra virgin olive oil, herbal teas and infusions are also very important for maintaining the right proportions of calcium and other minerals and avoiding imbalances or excesses. Do not forget the water, which in this case must be absolutely low in minerals.
The role of nutrition in the assimilation of calcium