Constipation - Causes and Diagnosis
Constipation (or constipation) is a discomfort that affects the mechanism of defecation. It is a symptom and not a real pathology, as constipation is often secondary to:
- anatomical - functional alterations of the intestine (hemorrhoids, fissures, diverticulosis / diverticulitis, rectocele, Crohn's disease, colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, etc.),
- other endocrine or metabolic diseases,
- pregnancy (see constipation in pregnancy)
- incorrect lifestyle and / or unbalanced diet (see diet and constipation),
- disorders / discomforts of the psychological sphere
- drug treatments (see drugs that cause constipation) etc.
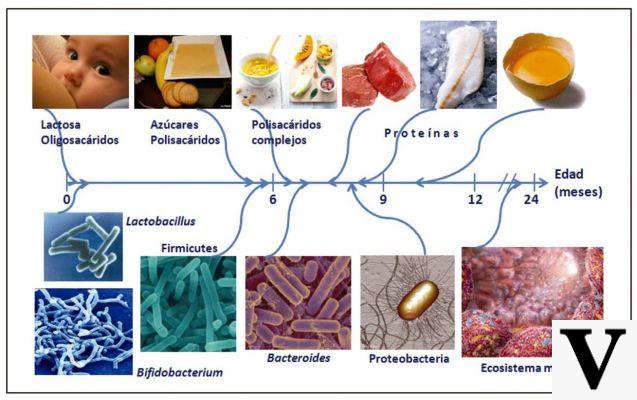
 Constipation affects boys more than girls in childhood, more girls than boys in adulthood, and more elderly than young people. In the neonatal period or in any case prior to weaning, constipation is not always linked to a concrete problem of evacuation; often, in fact, there is such a high absorption of meals (liquids), that the volume of waste is decidedly reduced.
Constipation affects boys more than girls in childhood, more girls than boys in adulthood, and more elderly than young people. In the neonatal period or in any case prior to weaning, constipation is not always linked to a concrete problem of evacuation; often, in fact, there is such a high absorption of meals (liquids), that the volume of waste is decidedly reduced.
The diagnosis for constipation requires the recognition of at least 2 out of 5 of the following factors, for a duration of 12 weeks (even non-consecutive), to be evaluated over a period of about one year:
- less than two weekly evacuations;
- difficulty and effort in evacuation;
- hard consistency of faeces or goat feces (segmented) or ribbon-like faeces (thin and flattened);
- feeling of blockage and / or constipation and / or incomplete evacuation
- need for manual help to complete fecal expulsion.
Constipation is often accompanied by short temper and asthenia, significantly compromising the quality of life of those who suffer from it.
Most of the time, constipation is idiopathic (i.e. not related to a disease) and becomes chronic due to: inadequate diet, sedentary lifestyle, pregnancy (uterine dislocation and hormonal profile mutation) and irritable bowel syndrome (disorder not yet well framed). If so, how can we intervene to prevent and treat constipation? Simple, with physical activity and a healthy and correct diet "
Intestinal motility is involuntary (peristalsis), while evacuation is a voluntary act (defecation). In constipation, often there is an alteration of the colic peristalsis and a mutation of the fecal expulsion process.
Treatment
Why does constipation arise? How to cure it?
Peristalsis is a movement that affects the entire digestive tract in a differentiated manner. In the intestine, peristalsis differs in 2 types of contraction:
- segmentation or mixing: it promotes the action of the intestinal bacterial flora and facilitates the absorption of vitamins, water and salts still present in the stool
- advancement or mass: moves the fecal mass up to the rectum, where the process of evacuation or defecation is activated.
The mechanism of displacement of the enteric contents from the descending colon to the rectum occurs thanks to the alignment between the sigmoid portion and the rectal ampulla, where the stool is contained before expulsion. The evacuation / defecation (which, as anticipated, is a voluntary process) takes place thanks to the perception of the sensation of fullness that triggers the relaxation of the pelvic floor and the anal sphincter; the process can be facilitated by the increase in intra - abdominal pressure generated by the contraction of abdominal muscles and by the Valsalva maneuver. The squatting position "Turkish style" (or with a stool under the feet) facilitates a physiological increase in intra-abdominal pressure, favoring defecation.
In idiopathic constipation, the problem is often localized "upstream" of the process and generically affects daily habits and lifestyle. In many cases, people with constipation are unaware of devote to this practice so important a time insufficient. Furthermore, the frenzy of everyday life easily distracts attention from bodily stimuli (not only with regard to defecation, but also with regard to thirst, appetite, etc.). Upon awakening and after meals (for different reasons) defecation should be facilitated compared to the rest of the day; needless to mention that in the morning, after breakfast and lunch, people have less time available than at other times of the day. By correcting these habits it is therefore desirable that the frequency of bowel movements increases, reducing the extent of constipation.
L'physical activity prevents and, in some cases, significantly contributes to treating constipation. Not only an active lifestyle, but also desirable physical and motor activity have a positive effect on intestinal peristalsis. The sport, as we know, it is a powerful anti-stress; it goes without saying that such activities can reduce the psychological and emotional distress responsible for the "block" of the evacuation. Furthermore, from the organic point of view, the vibrations (eg the impact on the ground of the race) and the abdominal muscle contractions act on the intestine like a real massage in favor of fecal progression. Not least, the release of cholinergic hormones; these molecules interact with the digestive tract favoring its contraction. Curious to note that, in parallel, also psychological, emotional and muscular relaxation (albeit diametrically opposed to motor activity) can prevent constipation; particularly significant examples are all activities such as mental training, meditation, etc. The most effective is undoubtedly yoga which, in association, involves the adoption of diaphragmatic breathing techniques (pranayama) responsible for visceral massage (on the liver, spleen and, as an anti-constipation, also on the large intestine. ).
Once it has been ascertained that constipation does not depend on the factors listed above, it is possible to analyze and possibly intervene on the mechanisms of food transit. The stool progresses in the intestine thanks to peristalsis, which is activated following the pressure and nerve response of the digestive tract. Consequently, the greater the fecal volume, the more frequent and effective the contractions are. The stool volume it is determined by the amount of waste / residue / undigested content in meals and the presence of water; moreover, the activation of the intestinal bacterial flora is followed by the production of gases that participate in the increase in intraluminal pressure. The nutritional component that "by definition" contains waste is dietary fiber. In summary: good quantities of dietary fiber and water in the meal, together with the right concentration of physiological bacteria in the intestine, determine hydration and fermentation (with the production of vitamins and other useful molecules, in addition to shielding from harmful agents), then the bulge, of the stool. This condition triggers the peristaltic contractions of mixing (which further promote the action of the bacterial flora) and, facilitating the advancement of the mass, speeds up the transit allowing the filling of the rectal ampoule. The soft consistency of the stool prevents constipation and the onset of hemorrhoids, fissures (often related to the pushing maneuver in Valsalva) and, indirectly, the likelihood of intestinal neoplasms.
Diet for constipation
Let's carefully analyze the 3 elements that boast the best "anti - constipation" function: dietary fiber, water and intestinal bacterial flora.
Dietary fiber against constipation
Dietary fiber is a set of molecules NOT digestible for humans, contained in plants and mushrooms. They can be classified as soluble and insoluble, or even better in viscous and non-viscous. Both, through different mechanisms, act positively against constipation. Those that produce an aqueous gel (the viscous ones) increase the volume of the faeces themselves, while those that, by fermenting, produce gas, increase the intraluminal pressure. While the former do not directly increase the transit speed but help to preserve the hydration (therefore the mass) of the stool, the non-viscous fibers cause a smooth muscle contraction reaction (segmentation and advancement) accelerating the overall movement. Furthermore, by acting as a substrate for bacterial fermentation, the fiber assumes the role of pre-biotic and improves the production of vitamins and other molecules useful for the organism.
The distinction between the two types of fiber is not simple and, to tell the truth, in practice it leaves the time it finds. Vegetables, fruit, algae, cereals, legumes and mushrooms contain (in variable percentages) both types of dietary fiber and in the daily estimate it is first of all necessary to reach 30g TOT (recommended ration also for healthy adults). From here, it is still possible to gradually increase it, while remembering that fiber (together with other molecules contained in the same foods) also has an ANTI - nutritional function by chelating mineral salts (especially calcium, iron and selenium).
Water against constipation
In the absence of water, even the intake of fiber could be in vain (or even counterproductive). Its function of diluting, gelifying and kneading the contents of the faeces has a not indifferent anti-constipation action. The lack of water in the stool does not allow the increase in volume and hinders the action of the intestinal bacterial flora, compromising peristalsis. Moreover, the lack of overall body hydration increases the water absorption of the large intestine, increasing the effect mentioned above.
For a diet against constipation it is therefore ESSENTIAL to introduce at least 1ml of water for every kcal taken with the diet, without forgetting that any increase in physical activity promotes the loss of fluids. They are excellent habits to combat constipation: carry water with you and remember to sip it from time to time during the day, drink at least 500-1000ml before, during and after physical activity (depending on the losses) and consume 1 or 2 glasses per meal.
Intestinal bacterial flora
it is now clear that the bacterial flora favors nutritional processing, the production of useful molecules and the preservation of the mucosal integrity of the intestine. It is genetically determined, but it is also influenced by lifestyle, drugs and nutrition. For some subjects it is very useful to increase their trophism by taking prebiotics (components of dietary fiber) and / or probiotics. The latter are marketed in the form of drugs, supplements and dietary foods. As far as food is concerned, it is not certain that they are concretely useful in preventing constipation since, undergoing the acid action of gastric juices, most of the live and active bacteria contained in them perish inexorably. On the other hand, an EFFECTIVE cure of probiotics (to be taken away from meals) by means of drugs or supplements, increases the density of the intestinal bacterial flora with the advantages we have already talked about.
lubrication of feces and intestines
The walls of the digestive tract are involved in physiological mucous secretion; this protective action reduces the friction between the fecal mass and the epithelium, favoring transit and reducing the possibility of abrasion. Foods also contain some molecules that have the same physical characteristic: lipids. They grease the faeces and the walls of the intestine by simulating the action of mucus. Sometimes, boosting lubrication or preventing it from shrinking can be a key factor in preventing and treating constipation. Readers will ask: "How can feces and intestines be lubricated?". Simple, ensuring a total fat intake between 25 and 30% of total calories.
Avoid Weight Loss Diets
We remind you that some good habits help a lot to fight constipation such as: eating a hearty breakfast (consisting of solid and liquid foods), avoiding the frenzy in eating meals and taking a seated and comfortable position during breakfast, lunch and dinner.
IMPORTANT! Finally, please note that certain weight loss diets are bad for the intestine, as they favor the onset of constipation. This reaction is due to several factors:
- Drastic reduction of fiber due to the deprivation of derivatives of cereals, legumes, fruit and, in the worst case, also of vegetables (which provide dietary fiber)
- Increase of dietary proteins at the expense of fats and carbohydrates: fats, as anticipated, act as lubricants and their absence / deficiency determines the increase of mechanical friction in the digestive tract. At the same time, carbohydrates (like fiber) have a marked prebiotic function and any depletion compromises the activity of the intestinal bacterial flora; moreover, the protein excess does NOT favor the trophism of physiological colonies and, often accompanied by ketosis, causes body dehydration with aggravation of constipation
- Reduction of water contained in food: a large part of the total water is supplied by food; reducing the portions a lot and not compensating with that drunk, the total water could be insufficient and promote the onset of constipation
Useful Foods
Then they exist foods that are suitable more than others to the diet for constipation. Among these we highlight: fruits and seeds, leaves, flowers, stems and roots. More specifically, they are excellent against constipation: whole legumes, whole grains and derivatives, artichokes, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, apples, pears, carrots, chicory, avocado, carob, chestnuts, feijoa, figs, prickly pears , guava, raspberries, macadamia, dried fruit (but with small portions), blueberries, blackberries, olives, passion flowers, currants, etc. They perform very well the anti - constipation function both in raw and cooked form. Cooking promotes food digestibility and promotes partial hydrolysis of some types of fiber, on the other hand, the process must NOT deprive the food excessively of water. The optimal combinations between the foods indicated above are of a mixed and cooked nature, i.e. soups, minestrone, past, caponata etc.
However, despite the very high fiber content, the intake of some foods is NOT considered positive against constipation. For example, the use of dehydrated fruit (NOT found in water) could have such a strong osmotic effect that it does not improve the disorder and, in some cases, risks making it worse.
Foods Not Recommended
The foods CONTRAINDICATED for constipation, on the other hand, are all those excessively processed, refined and dry; some examples are dried meat, crackers, breadsticks, taralli, fried snacks, sausages, salted meats, citrus juice (NOT whole citrus fruits), banana etc.
Finally, it must be specified that, in general, nervine drinks do not directly promote constipation even if, in the case of ethyl alcohol, there is a marked tendency to body dehydration, which inexorably affects the aggravation of constipation. On the contrary, in some cases, ethyl alcohol can irritate the intestine to the point of causing diarrhea; this is misinterpreted as a relief by constipation sufferers. On the other hand, it involves a rebound effect that occurs only a few hours after the episode.
Useful supplements
As for the products capable of moderating constipation, we would like to point out as of now that no distinction will be made between drugs and supplements; for more information about it, we recommend reading the dedicated article: Cures for constipation.
The products considered curative for constipation, as they facilitate defecation, are many and belonging to different categories.
ATTENTION! Prolonged use of some laxatives can determine the body adaptation and the reduction of the efficacy of the product itself; moreover, some laxatives act through chemical-physical mechanisms that are not entirely "healthy" for the intestinal mucosa and their use is recommended ONLY in case of strict necessity.
- Fiber and lactulose: nutritional components that act by increasing the volume and intraluminal pressure; they can lead to excessive onset of gas
- Osmotics: they increase the fecal volume by absorbing water from the surrounding environment (sometimes even from the intestine itself); they can cause dehydration and abdominal cramps
- From contact: they block intestinal water absorption and can cause dehydration
- Emollients: lubricants for faeces and intestines; they can cause oily leaks from the anus.
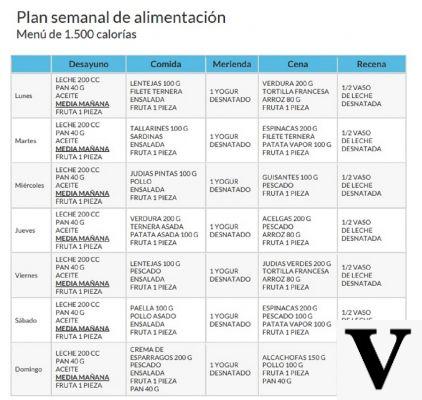
See an Example Diet Against Constipation "